Imagine you're approaching the peak physical condition you've always dreamed of, pushing your limits with each workout. You feel the burn in your muscles, the satisfying ache of effort. But also, that feeling of being 'tapped out' is starting to go deeper than just muscle soreness. It's like your internal wiring is frayed, making even familiar tasks feel harder. This sensation hints at a crucial aspect of performance and recovery: nervous system fatigue.
Just like your muscles can get tired, so too can the intricate network of nerves that control them and coordinate your entire body. So, let’s journey into the vital role your nervous system plays in every rep, stride, and recovery moment. From orchestrating the precise movements that define your peak performance to dictating how your body responds to the stress of a challenging workout (and ultimately signaling its need for rest), your nervous system is constantly at work. It's the key to training smarter, recognizing precisely when to push your limits, when to prioritize recovery, and ultimately, unleashing the full athletic potential you've always dreamed of.
Just like your muscles can get tired, so too can the intricate network of nerves that control them and coordinate your entire body.
What is the role of the nervous system in exercise?
The nervous system is the unsung hero orchestrating every facet of physical exercise, from the initial decision to move to the intricate coordination of muscle contractions and the physiological adjustments that sustain activity.
The initiation of exercise begins in the brain's motor cortex, a specialized region within the CNS where conscious commands are generated. These signals, electrical in nature, travel down the spinal cord via motor neurons, the specialized nerve cells responsible for transmitting movement instructions. Upon reaching the muscles, these signals trigger the release of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, at the neuromuscular junction.
This chemical signaling initiates the cascade of events within the muscle fibers that ultimately lead to contraction and movement. The precision and force of these contractions are meticulously controlled by the nervous system, allowing for the execution of complex movements, from the delicate adjustments required for balance to the powerful bursts needed for sprinting.
Beyond voluntary control, the nervous system also plays a critical role in regulating the body's physiological responses to the increasing demands of exercise. Similar to a 'fight or flight' response, the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system becomes dominant during exercise, leading to the release of catecholamines, which increase heart rate and contractility, dilate airways to improve oxygen intake, and redirect blood flow from less active organs to the working muscles, ensuring an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Furthermore, the nervous system is crucial for sensing the body's internal state during exercise and relaying this information back to the brain. Sensory receptors in muscles, tendons, and joints, known as proprioceptors, provide continuous feedback on muscle length, tension, and joint position. This proprioceptive information is processed by the brain and spinal cord, allowing for adjustments in muscle activation to maintain balance and coordination and prevent injury. For instance, the stretch reflex, mediated by the nervous system, automatically contracts a muscle when it is stretched too quickly, protecting it from overextension.
In the recovery phase following exercise, the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system becomes more active, promoting a return to a resting state. Heart rate and breathing slow down, blood pressure decreases, and energy is conserved. The nervous system facilitates the repair and adaptation processes that occur in response to exercise training, leading to improvements in strength, endurance, and coordination over time.
In essence, the nervous system is not merely a passive conduit of commands during exercise but an active and dynamic regulator, constantly sensing, integrating, and responding to the ever-changing demands of physical activity. Its intricate control and adaptive capabilities are fundamental to our ability to move, sustain exertion, and ultimately benefit from the myriad positive effects of exercise.
Your nervous system: a brief introduction
First, let's get acquainted with the body's remarkable communication network: the nervous system. Think of it as the intricate wiring that allows your brain to talk to every corner of your body and vice versa.
This vast network is broadly divided into two main parts:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS) is The Command Center: This is the body's control hub, comprised of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain, the body's processing powerhouse, analyzes information and generates commands. The spinal cord acts as the main communication highway, relaying signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is The Body's Messenger Network: Extending outwards from the CNS is the PNS, which consists primarily of nerves. These nerves are like bundles of long cables, known as axons, that stretch to every other part of your body – from your fingertips to your toes and all your organs.
Within these nerves, there are two main types of communication lines:
- Motor Nerves (Efferent): These nerves carry signals away from the CNS, delivering instructions from the brain and spinal cord to your muscles and glands, telling them what to do (like move your hand or secrete a hormone). So, efferent = exiting the CNS.
- Sensory Nerves (Afferent): These nerves carry information toward the CNS, relaying sensory input from your body (like touch, temperature, or pain) back to the brain and spinal cord for processing. So, afferent = arriving at the CNS.
The PNS itself has specialized branches that handle different types of bodily functions:
- The Somatic Nervous System: This is the part you're mostly consciously aware of. It controls your voluntary movements, like walking or writing, by sending signals to your skeletal muscles. It also receives sensory information from your skin, muscles, and joints.
- The Autonomic Nervous System: This system operates largely without your conscious control, managing essential automatic functions like heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It has three key divisions:
- The Sympathetic Nervous System: Often called the 'fight-or-flight' system, it kicks into high gear during stressful or emergency situations. It mobilizes the body's energy resources, increasing heart rate, elevating blood pressure, heightening alertness, and redirecting blood flow to skeletal muscles.
- The Parasympathetic Nervous System: This is the 'rest and digest' system. It's most active when you're relaxed, helping to slow down heart rate, decrease blood pressure, promote digestion and shift towards energy conservation and restorative processes.
- The Enteric Nervous System: Sometimes referred to as the 'second brain,' this intricate network of nerves is located within the walls of your gastrointestinal system. It primarily controls digestion, from the movement of food to the secretion of digestive enzymes, operating somewhat independently but also communicating with the rest of the nervous system.
Finally, we can also categorize nerves based on where they originate:
- Cranial Nerves: These nerves emerge directly from the brain and primarily serve the head and neck region, although some extend to other parts of the body.
- Spinal Nerves: These nerves branch out from the spinal cord and serve the rest of the body, connecting the CNS to the limbs and torso.
Understanding this basic framework of the central and peripheral nervous systems, with their specialized components, will be helpful as we explore how these systems are involved in various bodily processes discussed in this article.
Enjoying this article? Subscribe to Polar Journal and get notified when a new Polar Journal issue is out.
Subscribe
Why the nervous system one of the best indicators of stress and recovery status
Imagine your body is a high-performance vehicle, and the nervous system is its sophisticated diagnostic panel. When stressors hit – be it a grueling workout or a demanding week – this panel immediately registers the shifts. Unlike other systems that might show delayed responses, the nervous system offers a real-time, intricate readout of your internal equilibrium, making it an unparalleled barometer for both the acute pressures you face and your subsequent journey back to optimal recovery. Let’s look at how this happens.
When the body encounters a stressor – be it physical exertion, psychological pressure, or environmental change – the nervous system orchestrates a swift and multifaceted response. To initiate its 'fight-or-flight' response, the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system springs into action, triggering the release of catecholamines (natural stimulants) like epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine.
These immediate changes, readily measurable through indicators like heart rate variability (HRV) and electrodermal activity (EDA), provide a real-time snapshot of the body's acute stress response. For example, lower HRV, indicating reduced parasympathetic influence and dominance of sympathetic activity, often correlates with heightened stress levels. Similarly, increased EDA reflects heightened sympathetic arousal.
Beyond these immediate responses, chronic stress leaves a more enduring imprint on the nervous system. Prolonged activation of the stress response can lead to dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a key neuroendocrine system intricately linked with the nervous system. This dysregulation can manifest as altered baseline levels of stress hormones like cortisol and changes in the sensitivity of neural receptors. Furthermore, chronic stress can impact neurotransmitter balance in the brain, potentially leading to alterations in mood, sleep patterns, and cognitive function – all of which are regulated by neural circuits.
Conversely, the nervous system also provides clear signals of recovery. As the stressor subsides and the body returns to a state of homeostasis, the parasympathetic nervous system takes precedence. As this 'rest-and-digest' branch relaxes you, the increase in HRV, particularly from vagal nerve activity (the main nerves of your parasympathetic nervous system), is a strong indicator of improved recovery and enhanced physiological flexibility. You may feel calmer, with improved sleep quality and a sense of well-being, all mediated by neural processes, further corroborating a state of recovery.
undefined
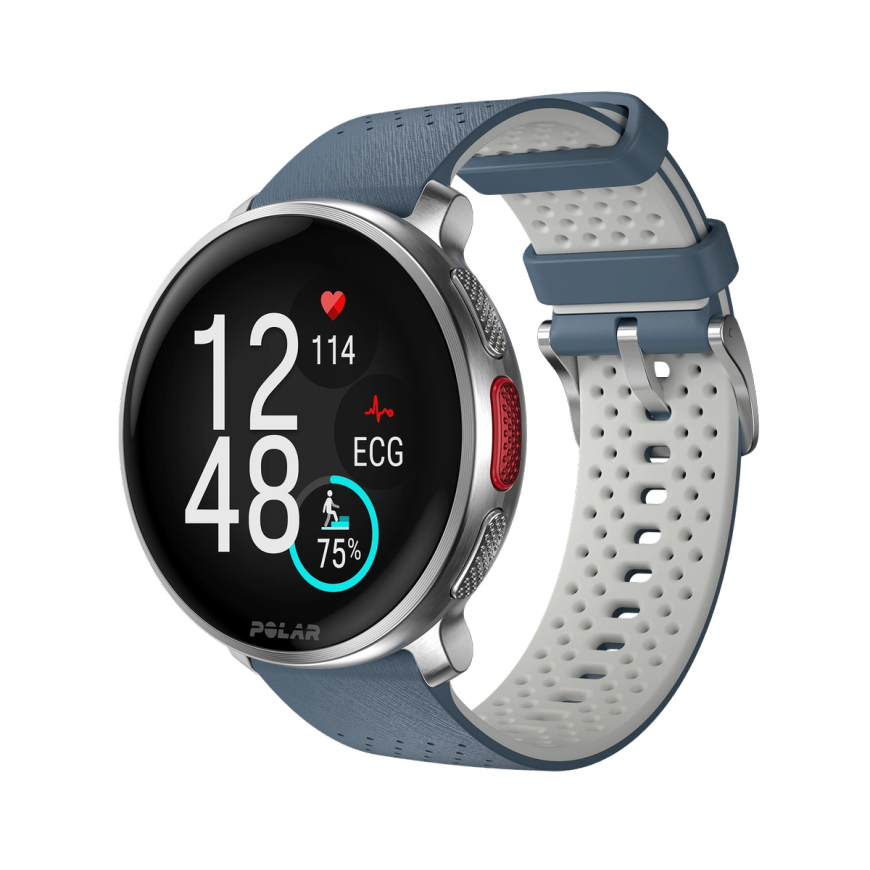

Polar Vantage V3
Premium Multisport Watch
An ensemble of biosensing instruments, AMOLED display, dual-frequency GPS, maps, and the most comprehensive suite of training and recovery tools on the market. The stage is set, and the Polar Vantage V3 smart sports watch is ready to put in the performance of a lifetime.
Signs of nervous system fatigue
Nervous system fatigue, a state of reduced efficiency in neural function, manifests in various ways both during and after physical exertion, as well as in other contexts of prolonged demand. Recognizing these signs is crucial for understanding your body's limits and promoting adequate recovery.
During exercise, the initial signs often point towards central or CNS fatigue (a decrease in the voluntary activation of muscles). This can present as a waning motivation to continue, even if the muscles still possess some capacity. Individuals might experience an increased perception of effort, where the same level of exertion feels significantly harder than usual. There can also be a slowing of reaction time and a decline in coordination, indicating a reduced ability of the brain and spinal cord to efficiently control movement.
As exercise continues, or in cases of intense activity, the nervous system's ability to effectively stimulate muscles can also become compromised, contributing to peripheral or PNS fatigue (a decrease in muscle action potentials). This may manifest as a decrease in muscle power output and a feeling of the muscles simply not responding as quickly or forcefully as before. Tremors or an inability to maintain fine motor control can also emerge.
Beyond the realm of exercise, the nervous system can become fatigued due to prolonged mental exertion, sleep deprivation, or chronic stress. In these contexts, the signs often overlap with central fatigue experienced during exercise. Individuals may notice difficulty concentrating, impaired memory and decision-making, and a general feeling of mental exhaustion or 'brain fog.' Irritability, mood swings, and a reduced capacity to handle stress can also be indicative of an overtaxed nervous system. Physical manifestations can include persistent low energy levels, headaches, and even disruptions in sleep patterns, further exacerbating the fatigue.
Recognizing the diverse manifestations of nervous system fatigue, both during exercise and in daily life, is critical for effective management. Coming up in the final section, we’ll delve into how technologies like Polar's Nightly Recharge feature can provide actionable insights into autonomic nervous system activity, thereby quantifying fatigue and recovery status (essentially: doing the hard work for you).
How do rest and deload weeks can help recover the nervous system?
As we've seen, the intricate demands of physical activity, particularly intense or prolonged exercise, place a significant load on the nervous system. Because both the CNS and the PNS can experience fatigue, the strategic implementation of rest periods and deload weeks becomes crucial for facilitating nervous system recovery, optimizing performance, and preventing overtraining.
Adequate rest, particularly sufficient sleep, is fundamental for CNS restoration. During sleep, the brain engages in vital processes, including clearing metabolic byproducts that can accumulate during neural activity. Neurotransmitter levels, which can become depleted or imbalanced with intense training, are also replenished. This allows for restoring optimal neural signaling efficiency, improving focus, motivation, and the ability to generate strong motor commands. Short, strategic rest periods between sets during exercise also allow for partial recovery of the neuromuscular junction, the site where nerve signals communicate with muscle fibers, ensuring sustained force production.
Deload weeks, typically involving a planned reduction in training volume and intensity, provide a more extended window for nervous system recuperation. By decreasing the overall stress on the body, including the neural demands of intense muscle activation and coordination, deloads allow the CNS to recover its baseline excitability. This can manifest as a reduction in perceived effort during subsequent training, improved reaction time, and enhanced neuromuscular coordination. Furthermore, deloads provide an opportunity for the PNS to recover its capacity for efficient signal transmission to the muscles, potentially mitigating peripheral fatigue and improving contractile strength in the long term.
The benefits of rest and deload weeks extend beyond simply alleviating fatigue symptoms. By allowing the nervous system to recover fully, these periods can enhance the body's adaptive response to training. A well-rested and responsive nervous system is better equipped to drive muscle protein synthesis, improve motor unit recruitment (the activation of muscle fibers by motor neurons), and facilitate the development of strength and power. Neglecting nervous system recovery, on the other hand, can lead to a state of chronic fatigue, increased risk of injury, and diminished training adaptations, highlighting the critical role of strategic rest and deloading in a comprehensive training program.
Which type of metrics should you be monitoring?
We've talked about the ‘hidden signals’ your nervous system sends, hinting at its fatigue or readiness. The good news? You don't need a lab coat to detect them. Thanks to the smart technology packed into modern wearables, these once-elusive signs are now readily accessible. By simply wearing a device, you can passively gather crucial data about your body's recovery status.So, let's explore these simple, yet powerful metrics that you can easily monitor.
1. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
As mentioned above, this metric measures the variation in time between successive heartbeats. A higher HRV generally indicates a more recovered and adaptable nervous system, with a better balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system. Polar's Orthostatic Test is a specific feature that measures HRV in different body positions (lying down and standing) to assess cardiovascular and autonomic recovery. Regularly using this test can help establish your baseline HRV and identify deviations that might signal under-recovery or overtraining. A significant drop in your typical HRV after a workout or over several days could indicate that your nervous system is still under stress and needs more recovery.
2. Sleep Metrics
Sleep is a crucial period for nervous system restoration. Polar's sleep tracking features, such as Sleep Plus Stages, provide detailed insights into sleep duration, quality, and time spent in different sleep stages (light, deep, REM). Adequate deep sleep is particularly important for physical and mental recovery. Features like Nightly Recharge™ go a step further by combining sleep data with an assessment of your autonomic nervous system's activity during the early hours of sleep. This provides a comprehensive overnight recovery score, indicating how well your body and nervous system have recovered from the previous day's strain. Consistently poor sleep scores or disruptions in sleep stages can be a strong indicator of nervous system stress.
3. Training Load Pro
This Polar feature quantifies the strain from your workouts on different body systems, including the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems. It also incorporates your perceived exertion. While not a direct measure of nervous system fatigue, consistently high training loads without adequate recovery can lead to nervous system overload over time. Monitoring your Cardio Load and Muscle Load in relation to your recovery metrics can help you understand if the overall stress on your body, including the neural demands of training, is being adequately managed. If your training load consistently trends upwards while your HRV and sleep metrics decline, it suggests your nervous system might be struggling to keep up with the demands.
By consistently monitoring these metrics provided by Polar sports watches, individuals can gain valuable insights into their nervous system's recovery status. Observing trends and understanding how training load, sleep, and HRV interact can empower informed decisions about training intensity, rest days, and deload weeks, ultimately leading to better performance and a reduced risk of overtraining.
 Polar Vantage M3
Polar Vantage M3
 Polar Grit X2 Pro Titan
Polar Grit X2 Pro Titan
 Polar Grit X2 Pro
Polar Grit X2 Pro
 Polar Grit X2
New
Polar Grit X2
New
 Polar Vantage V3
Polar Vantage V3
 Polar Ignite 3
Polar Ignite 3
 Polar Ignite 3 Braided Yarn
Polar Ignite 3 Braided Yarn
 Polar Pacer Pro
Polar Pacer Pro
 Polar Pacer
Polar Pacer
 Polar Unite
Grit X Series
Vantage Series
Pacer Series
Ignite Series
Polar Unite
Grit X Series
Vantage Series
Pacer Series
Ignite Series